PCR Vs Antigen
PCR tests are considered the “gold standard” of testing as they are extremely sensitive and good at detecting the presence of the virus at extremely low levels of viral load. Because these tests can detect viral fragments even without virus, individuals will likely test PCR positive long after they have transmissible virus. According to Harvard School of Public Health Professor Michael Mina, MD, PhD, 40-80% of the time a patient is PCR positive, the individual is post infectious. Though sensitive and good at detecting if a person was infected by the virus, PCR tests are expensive and slow, making them less than ideal when screening large populations.
Rapid antigen tests, on the other hand, are excellent at detecting infectiousness and decreasing community spread. Unlike PCR tests, rapid antigen tests are more affordable and provide results in 10-15 minutes, allowing for the ability for regular, widespread testing. In a study by the University of Colorado BioFrontiers Institute and Harvard Chan School of Public Health, when used twice a week, widespread rapid testing reduced the degree of infectiousness of the virus by 80%, compared to twice (2x) weekly PCR only testing (with 48 hour results), which reduced infectiousness by 58%.
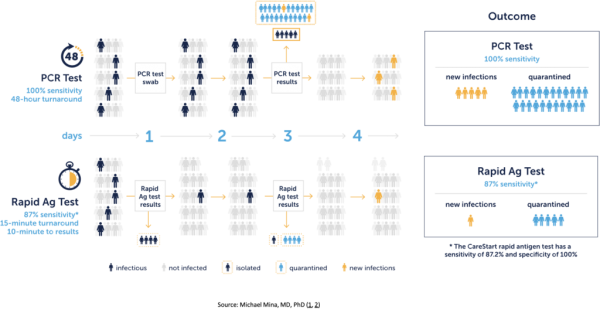
For population management, serial rapid testing is more effective than infrequent, PCR only testing.
Decreasing the degree of COVID population spread
Due to the frequency and timeliness of results, rapid antigen tests add value in triaging and contact tracing infectious individuals. These tests serve as a crucial screening tool and a key part to stopping COVID-19 from spreading. Frequent rapid antigen testing can reduce the degree of infectiousness of the virus considerably more than a PCR-only testing protocol.
Accessing rapid Covid tests for your workplace
Incorporating frequent rapid antigen tests into workplaces as a testing protocol can help slow the spread of COVID-19 in our population and provide a much needed risk management tool for workplaces providing quick and accurate results that provide a measure of contagiousness and reduce the rate of infection.


